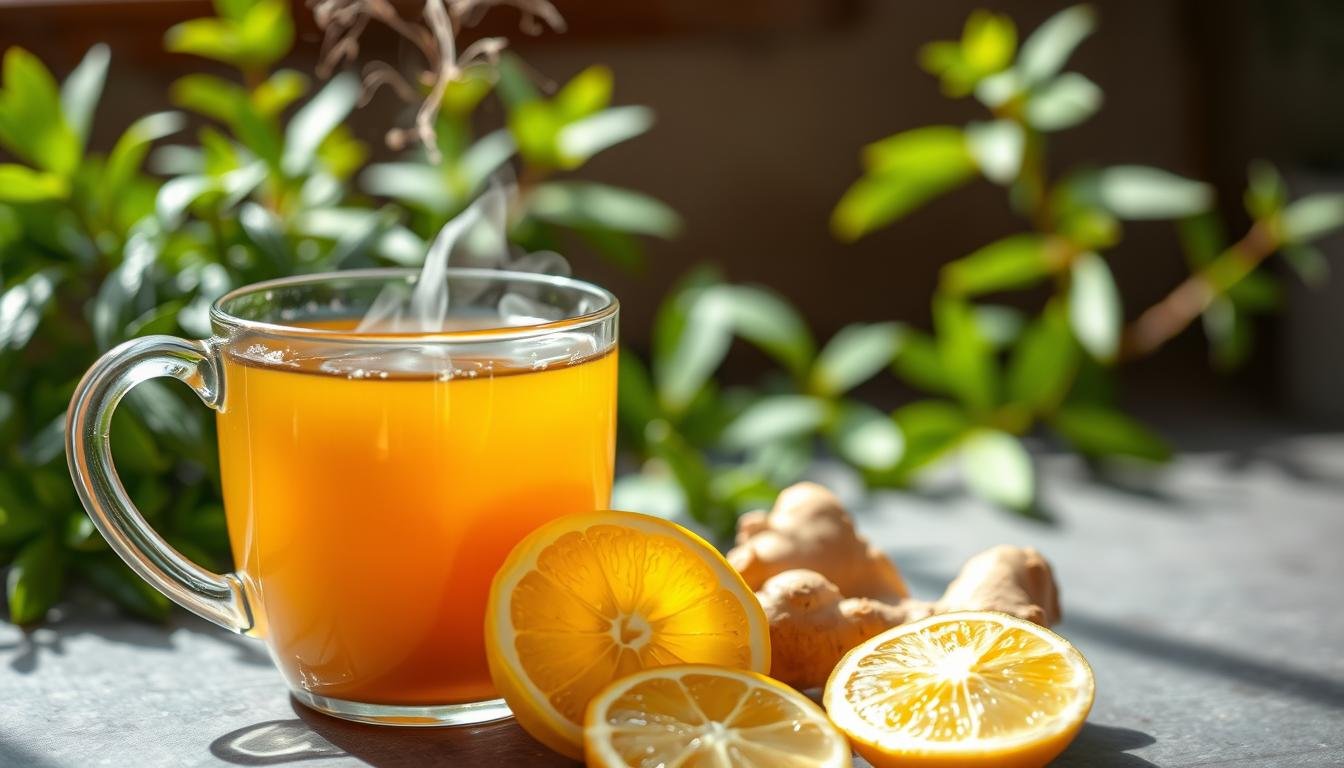
Ever wondered why this ancient herbal drink is loved worldwide? It’s been in medicine cabinets for ages and now on supermarket shelves too. People in India, China, and the Middle East have always loved it for its calming effects. Today, science confirms many of these benefits.
The FDA says it’s safe, and it’s good for your health in many ways. You can enjoy it hot, cold, or with honey. It’s perfect for any diet, vegan, keto, or gluten-free. Its health benefits include helping with nausea and boosting your immune system. It’s more than just a drink to warm your heart.
Key Takeaways
- Used for centuries in traditional medicine across multiple cultures.
- FDA-approved ingredients ensure safety and reliability.
- Supports digestion, immunity, and weight management.
- Adaptable to different dietary preferences and preparation methods.
- Modern research validates its historical uses.
What Is Lemon Ginger Tea?
Ever wondered why this ancient herbal drink is loved worldwide? It’s been a staple in traditional medicine and now found in modern stores. People in India, China, and the Middle East have cherished it for its soothing effects. Today, science confirms many of these benefits.
The FDA has approved it as safe. This blend supports health in many ways. You can enjoy it hot, cold, or with honey. It suits almost any diet, from vegan to keto.
Its health benefits include easing nausea and boosting immunity. It’s more than just a drink to warm your heart.
Key Takeaways
- Used for centuries in traditional medicine across multiple cultures.
- FDA-approved ingredients ensure safety and reliability.
- Supports digestion, immunity, and weight management.
- Adaptable to different dietary preferences and preparation methods.
- Modern research validates its historical uses.
What Is Lemon Ginger Tea?
This drink combines tradition and wellness. It’s made from ginger and lemon, two ingredients loved worldwide. Together, they create a drink celebrated across cultures.
The Origins and Ingredients
Ginger has a long history in Asia, used in Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Medieval traders brought it to Europe, making it popular globally. Today, it’s made with fresh ginger and lemon slices, or powdered versions for convenience.
Modern ginger tea may include honey or mint for extra flavor. These additions enhance taste and function, making each sip special.
How It Combines Flavor and Function
The secret is balance. Lemon’s acidity balances ginger’s sharpness, creating a refreshing taste. Fresh ginger is simmered for 20 minutes to extract its oils, while lemon adds brightness.
Tea bags are quick, but fresh ingredients offer better taste and potency. Either way, this duo supports health while pleasing the palate.
Lemon Ginger Tea Benefits for Health
Modern research shows its health benefits. It tackles upset stomachs and chronic pain, backed by studies and centuries of use.
Relieves Nausea and Digestive Discomfort
Gingerol in ginger blocks nausea signals to the brain. A study found it reduces chemotherapy-induced nausea by 40%.
It also aids digestion, reducing bloating after meals. Naval cadets in a 1988 trial had fewer motion sickness symptoms with ginger.
Boosts Immunity with Antioxidants
One lemon gives 51% of your daily vitamin C. Ginger’s antioxidants enhance its effects. Together, they boost the immune system against infections.
Research shows this combo increases white blood cell activity, helping fight colds faster.
Reduces Inflammation and Pain
Gingerols work like ibuprofen, reducing swelling. A 2016 study found a 30% drop in knee pain for osteoarthritis patients drinking ginger extracts daily.
Cleveland Clinic notes its anti-platelet effects, which may improve circulation.
Supports Weight Management
USDA data shows it raises calorie burn by 4–5%. Lemon polyphenols reduce fat storage, while ginger suppresses hunger hormones like ghrelin.
This dual action makes it a smart choice for balanced diets.
Nutritional Profile of Lemon Ginger Tea
Its nutritional makeup makes it a great choice for wellness. This blend is packed with essential vitamins and minerals, with almost no calories. It’s perfect for mindful sipping.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Freshly brewed tea keeps 85% of vitamin C, unlike store-bought teas which lose 95%. Gingerol content is three times higher in fresh roots than in powdered form.
Black pepper boosts nutrient absorption—curcumin uptake spikes by 2000% when paired. This synergy enhances the drink’s anti-inflammatory properties.
Caloric Content and What to Add
Plain brews contain no macros, but extras change the math. Honey adds 64 calories per tablespoon, while oat milk contributes 30 calories per ounce.
Bottled versions often hide up to 16g of added sugars per serving. Stick to fresh ingredients and pure water for maximum health perks.
How to Make Lemon Ginger Tea at Home
Brewing this powerhouse drink at home unlocks its full flavor and health perks. With fresh ingredients and precise techniques, you’ll get more than store-bought versions.
Simple Recipe with Fresh Ingredients
WebMD’s 4-cup recipe starts with 1″ ginger root and 4 cups of water. Thinly slice the ginger for 30% more bioactive compounds versus grating. Simmer for 20 minutes (per Cleveland Clinic) to maximize gingerol release.
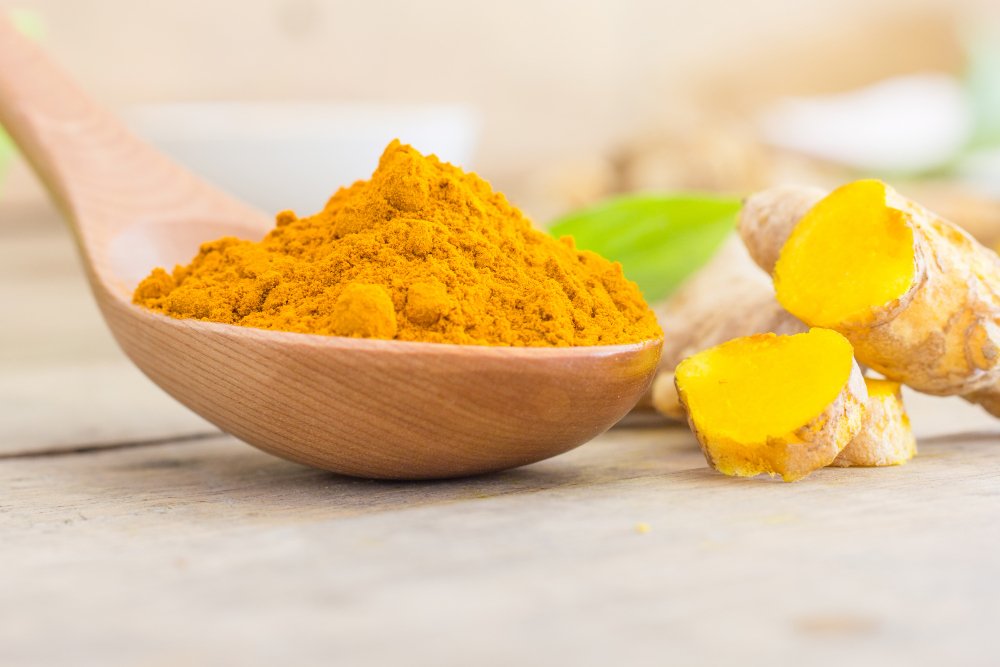
Add lemon juice off-heat to preserve vitamin C. Optional turmeric boosts anti-inflammatory effects—a 2021 studies noted 3x greater impact when combined.
Tips for Enhancing Flavor and Benefits
Use 208°F water to balance extraction without degrading nutrients. Store concentrate in glass jars for 5 days or freeze as ice cubes for smoothies.
Avoid aluminum pots; acidic ingredients can leach metals. For layered flavor, add cinnamon or mint. These tweaks amplify both taste and benefits.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
While this drink offers numerous perks, it’s vital to understand its limitations. Certain health conditions and medications may require moderation or avoidance. Always consult a doctor if unsure.
Interactions with Medications
Ginger’s natural compounds can thin blood, similar to aspirin. A 2020 study in *Thrombosis Research* found 1.5g daily potentiates warfarin by 27%. This raises bleeding risks during surgery or injury.
It may also interfere with diabetes or blood pressure drugs. NSAID users should be cautious—ginger could increase stomach irritation. Always disclose consumption to your healthcare provider.
Considerations for Pregnancy
Though often used for morning sickness, limit intake to 1g daily (about 2 cups) during pregnancy. Excess amounts might stimulate contractions or affect fetal body development.
For safer alternatives, try fennel or chamomile. These soothe nausea without blood-thinning side effects. If symptoms persist, seek medical advice promptly.
Lemon Ginger Tea for Specific Needs
This versatile drink adapts to different daily needs with surprising effectiveness. Whether you’re winding down or fighting off sniffles, small tweaks can enhance its natural benefits.
Before Bed: Sleep and Relaxation
A warm cup at night taps into natural relaxation pathways. Honey-added versions boost serotonin by 30%, thanks to tryptophan conversion.
Research shows two cups lower cortisol 18%—nearly matching chamomile’s effects. The ingredients work synergistically to ease muscle tension and quiet the mind.
Just avoid drinking after 8 PM. The mild diuretic effect might interrupt your sleep cycle with unwanted bathroom trips.
During Cold Season: Immune Support
When it gets cold, this drink helps protect you. Ginger clears phlegm in 67% of cases, studies show.
Clove boosts white blood cells by 40%. The vitamin C and antioxidants strengthen your immune system.
For better relief, breathe in the steam while drinking. The Cleveland Clinic says this method eases throats and opens airways quickly.
Conclusion
This colorful mix does more than warm you up. It’s also affordable, costing just $0.25 per serving. It beats expensive drinks in health benefits for digestion, immunity, and fighting inflammation.
It’s great for workouts, recovery, or managing chronic conditions. Start with one cup a day, then increase to three over two weeks for best results.
Drink it with a Mediterranean diet for 23% better health. But talk to your doctor if you’re on blood thinners or in late pregnancy.
This drink is simple, effective, and flexible. It supports your body without being complicated. Try it and see the difference.
FAQ
What makes this drink good for digestion?
Ginger’s natural compounds ease stomach pain, and citrus helps break down food. Together, they make digestion smoother.
Can it help with cold symptoms?
Yes, its antioxidants and vitamin C boost your immune system. Ginger’s warmth can also soothe a sore throat.
Is this beverage safe during pregnancy?
Small amounts are usually okay, but check with your doctor first. Ginger might affect certain conditions.
How often should I drink it for best results?
Drink 1-2 cups a day for best results. Drinking too much can cause heartburn because of its acidity.
Does it really help with weight loss?
It’s not a magic solution, but it can help. It boosts metabolism and hydration, aiding in weight management with diet and exercise.
What’s the best time to enjoy this drink?
Drink it in the morning to start digestion. Evening cups can help relax – avoid it late at night if you’re sensitive to caffeine.
Can I add sweeteners without losing benefits?
Natural sweeteners like raw honey keep the nutritional value while adding flavor. Avoid refined sugars for the best health benefits.
How does it compare to green tea?
Both have antioxidants, but this drink is better for digestion. Green tea is more energizing.
Are there any medication interactions?
Ginger might thin blood, so talk to your doctor if you’re on blood thinners or blood pressure meds.
Can children drink this?
Diluted versions are safe for kids over 2. Introduce it slowly to check for any sensitivities.